Essential Differences Between Spigot and Faucet
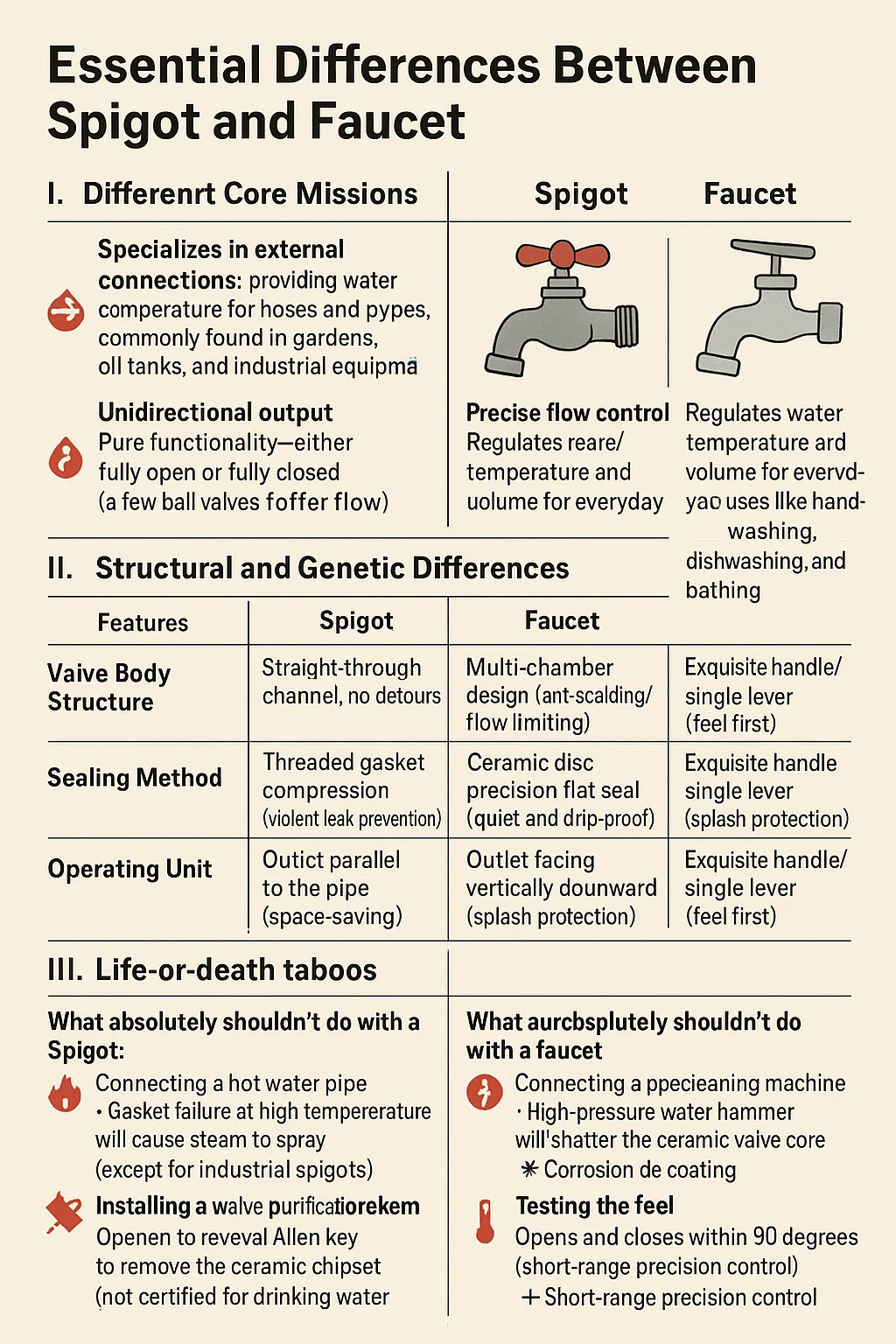
I. Different Core Missions
Spigot
Specializes in external connections: providing quick-connect connections for hoses and pipes, commonly found in gardens, oil tanks, and industrial equipment
Unidirectional output: Pure functionality—either fully open or fully closed (a few ball valves offer adjustable flow)
Faucet
Precise flow control: Regulates water temperature and volume for everyday uses like handwashing, dishwashing, and bathing
Mixed media: Built-in diverter valve core allows for mixing hot and cold water (Spigot is always single-ended)
II. Structural and Genetic Differences
| Feature | Spigot | Faucet |
|---|---|---|
| Body Construction | Straight-through flow (no detours) | Multi-chamber design (anti-scald/flow restrictor) |
| Sealing Method | Brute-force gasket crush (thread torque) | Ceramic disc precision seal (drip-free silence) |
| Outlet Orientation | Parallel to pipe (space-saving) | Vertical downward (anti-splash) |
| Operation | Stubby lever/handwheel (glove-friendly) | Sleek handle/single lever (ergonomic priority) |
| Pressure Handling | Raw pipe pressure (no dampening) | Built-in pressure compensator (steady flow) |
| Failure Mode | Gasket blowout under surge | Cartridge fracture if grit present |
III. Life-or-death taboos
What you absolutely shouldn't do with a Spigot: Connecting a hot water pipe → Gasket failure at high temperatures will cause steam to spray (except for industrial spigots) Installing a water purification system → Heavy metal precipitation (not certified for drinking water)
What you absolutely shouldn't do with a faucet: Connecting a pipe cleaning machine → High-pressure water hammer will shatter the ceramic valve core ️ Dispensing diesel fuel/acidic or alkaline solutions → Corrosion of the coating will clog the aerator
IV. Expert identification tips
Check the threads
Spigot: Male male connector (active attack)
Faucet: Female female connector (receptive acceptance)
Removing the valve core
Spigot: Open to reveal the rubber gasket and metal stem
Faucet: Use an Allen key to remove the ceramic chipset
Testing the feel
Spigot: Fully open after rotating beyond 270 degrees (force-saving lever design)
Faucet: Opens and closes within 90 degrees (short-range precision control)


 English
English русский
русский 日本語
日本語 عربى
عربى Español
Español












